

- #Refrigeration compressor capacity calculation how to
- #Refrigeration compressor capacity calculation software
#Refrigeration compressor capacity calculation software
Recently I used Copeland selection software to calculated ZS21k4E compressor capacity. Another benefit of it is that it will actually dry things as well as remove heat.I created this thread because I am really curious about compressor cooling capacity and I cannot find an answer in the Internet, meybe you will clarify this issue. For instance, a form of the refrigeration cycle occurs in the pasteurization of milk. The cycle also serves other industrial uses. So the power P in kilowatts (kW) is equal to the power P in refrigeration tons (RT) times 3.5168525: P (kW) P (RT) × 3.5168525. One kilowatt is equal to 0.284345 refrigeration ton: 1 kW 0.28434517 RT. One refrigeration ton is equal to 3.5168525 kilowatts: 1 RT 3.5168525 kW.
#Refrigeration compressor capacity calculation how to
The cycle’s flexibility to meet a variety of requirements means it is the most widely used for anything that needs cooling. kW to tons conversion calculator How to convert tons to kW. Likewise, reversing the refrigeration cycle induces heating into an environment. For instance, with a fridge the average cooling temperature is around 40° F whereas a freezer averages around 0° F. These units are also variable in cooling power. The commonly used cycle is incredibly useful and efficient at properly removing heat from an environment. Whether it is a window unit cooling an 80 sq ft room or a industrial-sized HVAC unit cooling an 16k sq ft warehouse.

Almost every building in modern countries has some form of an air conditioner. The refrigeration cycle functions in many shapes and sizes throughout the globe. Usually, the COP falls between 2.3 to 3.5 and serves as a rating of how efficient a refrigeration cycle is.Īpplicable Uses of the Refrigeration Cycle Next, the calculation of cooling load determines how much cooling work occurs in the cycle.įinally, we can use the cooling load and input power to find the Coefficient of Performance(COP).
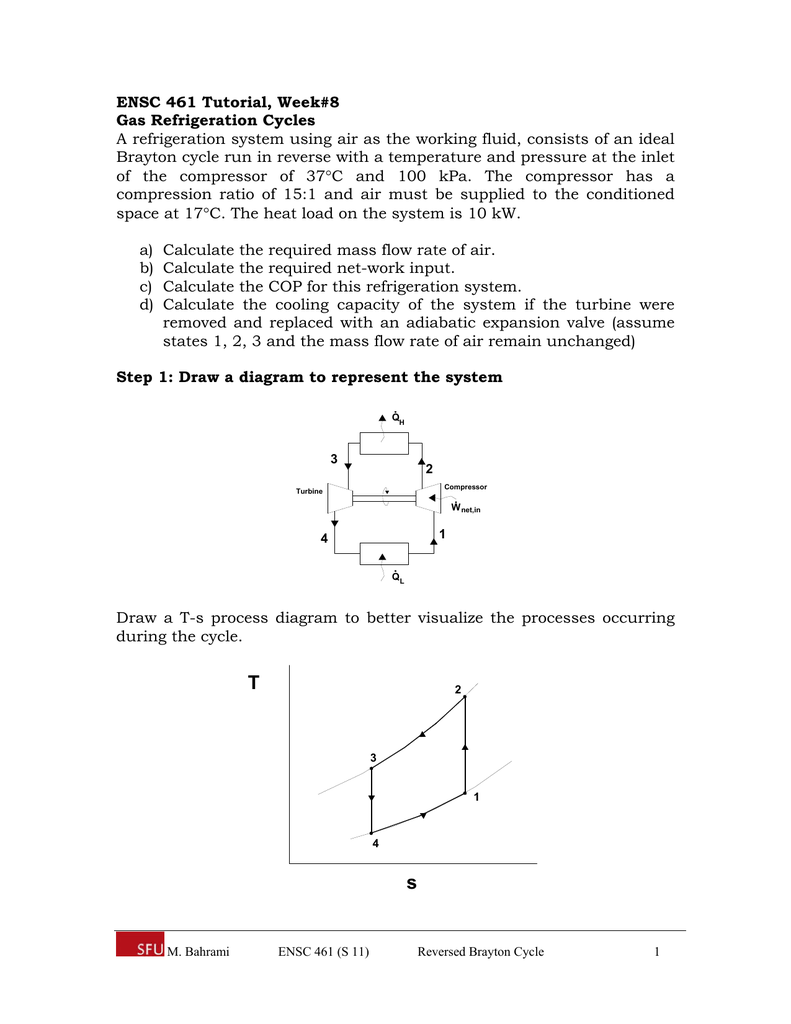
The mass flow rate( ṁ) of refrigerant also provides for these calculations, and might need to be defined or measured to find. First and most importantly, the calculation of the cycle’s power may occur. With all the enthalpies determined, the inner workings of the given cycle can be fully analyzed. Calculations of the Refrigeration Cycleīecause the process is throttling, the enthalpy( h4 = h3) remains constant throughout the expansion valve. The evaporator is the actual part of the cycle that does the cooling to the environment. Finally, the evaporator converts the cool refrigerant into a gas. So that the liquid can expand by reducing the pressure using an expansion valve. Next, the now hot refrigerant enters a condenser to become a hot liquid. The overall volume reduces and pressure raises, prompting a rise in temperature. The process begins by funneling some sort of refrigerant (commonly R-134), in gas form, through a compressor. These four devices are a compressor, condenser, some sort of expansion device, and evaporator. The refrigeration cycle consists of four main devices which work together to accomplish this goal. Unlike other cycles the goal is to remove heat from an environment using electrical work rather than turning heat into mechanical work. However the refrigeration cycle works by instead taking the inside air, removing the heat from the air by transferring it to a refrigerant and then returning the cool air. Because of the thermodynamic laws that heat can only flow from hot to cold, The cycle seems like it should not be able to cool a space. The refrigeration cycle works very differently than most thermodynamic cycles that exist. In this article, you will learn the principles behind the refrigeration cycle, calculations, and applications.

This cycle occurs in almost every modern building through the HVAC systems and indoor refrigerators. Likewise, it provides the exact opposite effect by simply reversing the cycle. The refrigeration cycle is a specially designed thermodynamic cycle that removes heat from a closed environment to keep the inside cool.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
